 |
|
IN THIS ISSUE:
» Dynamic Motor Power Measurement Enables In-Vehicle Testing Of EVs
» Field Solvers: A Different Perspective On EMI In Power Electronics
» How To Select Bridge Rectifiers
» Focus On Magnetics:
Magnetics Utilization Vs. Converter Topology: A Little Extra Silicon Goes A Long Way
» Spotlight On Safety & Compliance:
Selecting An AC Line Filter For Switching Power Supply Applications
» New Power Products
» Industry Events:
- Another Successful ECCE
» Other Top Power News
From the Editor's Desk David G. Morrison
Editor, HOW2POWER TODAY

Electric vehicles (EVs) are responsible for extensive, ongoing R&D on numerous power components and power conversion technology, and batteries of course. They are also inspiring the development of new power-related test instruments. In this issue, authors Mitch Marks and Mike Hoyer discuss the capability of new mobile power analyzer tools to make dynamic power measurements in vehicles for testing electric motors and drives under real-world driving conditions. The main development that makes these measurements possible is the move away from fixed-frequency 50/60 Hz power measurement, the method used in traditional power analyzers, to use of algorithms that can measure power on high-frequency, high-voltage inverter signals whose frequency is changing. The article also outlines other capabilities in the new tools such as a method of correlation and feedback to external systems, which are specifically intended to aid development of electrical and mechanical systems in EVs and hybrid vehicles. As the automotive EV market grows and similar trends of electrification take hold in aerospace, industrial vehicles and elsewhere, electronic instrumentation must keep pace. So expect more developments along these lines in power-related testing. This issue of the newsletter also presents articles on the need for field solvers for EMI simulation in power electronics, how to select bridge rectifiers and EMI filters, the impact of converter topology on transformer utilization, plus the latest power component news and more.
|
|
 |
 |

|
HOW2POWER EXCLUSIVE DESIGN ARTICLES 
|
Dynamic Motor Power Measurement Enables In-Vehicle Testing Of EVs
by Mitch Marks and Mike Hoyer, HBM Test and Measurement, Madison, Wisc.
In the emerging electric vehicle market, electrical power measurements on motors and related power conversion circuitry are becoming necessary to perform an evaluation of a vehicle. Mobile power measurement was previously difficult due to the dynamic nature of the vehicle speed. However, unique features provided in HBM’s eDrive, a system for testing electric machines and drives, make mobile electrical power measurements possible in real-world operating environments. After some initial discussion of why in-vehicle testing is needed, power measurement challenges, and the limitations of traditional power analyzers, this article will explain how eDrive performs dynamic power measurements and publishes cycle-based calculations to a CAN bus for correlation to an existing DAQ system, and the implications for testing EVs under real world conditions.
Read the article…
|
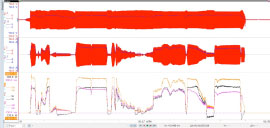
A series of dynamic power
measurements on an electric scooter
demonstrate how motor and drive
performance can be assessed during
vehicle acceleration and deceleration,
coasting and other conditions. |

Field Solvers: A Different Perspective On EMI In Power Electronics
by Paul L. Schimel, Microchip Technology, Chicago, Ill.
As computers and modeling improved, tools known as field solvers began to run Maxwell’s equations for complete circuits and board layouts for RF systems. Running Maxwell’s equations accounted for the parasitics, dielectrics, trace routing, plane layers, trace widths, thicknesses, etc. The ability to model and predict RF circuit behavior in this way cut down on design iterations, helping engineers to be more productive. In this article, the author argues that field solvers could soon have a similar impact on power electronics. Although there are differences between RF and power supply signals and circuits, power electronics engineers also care about fields, particularly when it comes to designing power circuits for low EMI and ultimately to meet EMC requirements. As field solvers continue to evolve, we could soon be using these tools to simulate the E and H fields our power circuits are generating, to the point of achieving first pass design success in EMC, as the author explains.
Read the article…
|

How To Select Bridge Rectifiers
by Jos van Loo, Taiwan Semiconductor Europe, Zorneding, Germany and Kevin Parmenter, Taiwan Semiconductor America, Chandler, Ariz.
Choosing to use a bridge rectifier in a design vs. discrete rectifiers is often a tradeoff in terms of space, size, cost or whatever the case may be. Sometimes pc board space and the insertion of a single component into the board (versus four) are the most important issues, other times not. Sometimes power levels dictate the use of a packaged bridge rectifier. This article assumes that the choice to use a bridge rectifier rather than discretes has already been made. Given that decision, what are the electrical and mechanical specifications that need to be considered and what are the designer’s options when selecting a bridge rectifier? In this article the authors identify the relevant specifications, outline the options, and offer advice on how to navigate the specs, quality and cost considerations.
Read the article…
|
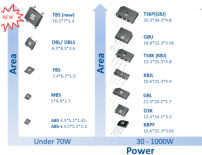
Sorting through the many package
options, and matching them with
your power, thermal and space
constraints is just one aspect of
selecting a bridge rectifier. |

 |  |

FOCUS ON MAGNETICS 
Sponsored by Payton Planar Magnetics
A monthly column presenting information on power magnetics design, products, or related technology |

Magnetics Utilization Vs. Converter Topology: A Little Extra Silicon Goes A Long Way
by Dennis Feucht, Innovatia Laboratories, Cayo, Belize
One of the goals of magnetics design is to achieve the greatest utilization possible from a magnetic component, to get the most use out of it as possible. Utilization, U, is defined quantitatively based on waveforms, usually current waveforms, as the average value of current (or voltage) divided by the peak value of current (or voltage). U expresses the extent to which a component is able to deliver the desired quantity, the average, relative to the maximum of that quantity that it must handle, or the peak rating. The ideal value is U = 1; the component need not be rated at any greater amount than what is used. Although the ideal of one is desired, the extent that it can be achieved varies based on the circuit of the magnetic component. In this article, we’ll examine four popular isolated power supply topologies—the flyback, forward, full bridge and half bridge converters—to see the impact that each has on utilization of the transformer. Read the full story…
|

 |
 |

SPOTLIGHT ON SAFETY & COMPLIANCE 
Sponsored by Power Integrations
A monthly column discussing standards and regulatory requirements affecting power electronics |

Selecting An AC Line Filter For Switching Power Supply Applications
by Kevin Parmenter, Chair, and James Spangler, Co-chair, PSMA Safety and Compliance Committee
While guidelines have been written on how to select EMI line filters, many system engineers still aren’t aware that they need EMI filters. When they do realize they need one, they often select a filter without regard to their actual filtering needs. They may also ignore the impact of the filter on other requirements (such as leakage current), and issues such as customer support. In this article, the authors identify some of the popular bad practices being used to choose EMI line filters, explain why they’re wrong and provide a quick guide to proper filter selection that will help designers avoid the common pitfalls. They identify the key criteria you’ll need for filter selection including rules of thumb and key specs that will guide designers in making good choices. Armed with this information, designers will be better equipped to apply the EMI selection guides and tools already available. Read the full article…
|

 |
 |

 — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS — POWER PRODUCTS IN 3 IMAGES OR LESS 
|

|

Teledyne LeCroy’s MDA 8000HD
Motor Drive Analyzers. |
Motor Drive Analyzers Create A 16-Channel Data Acquisition System
 Photo: The company’s OscilloSYNC technology breaks channel-count barriers by teaming two MDA 8000HD instruments to view and control 16 synchronized analog channels from a single display and front panel. Like the earlier MDA800A, this iteration performs comprehensive static and dynamic three-phase electrical and mechanical power analysis and complete test coverage of the entire motor-drive system. Photo: The company’s OscilloSYNC technology breaks channel-count barriers by teaming two MDA 8000HD instruments to view and control 16 synchronized analog channels from a single display and front panel. Like the earlier MDA800A, this iteration performs comprehensive static and dynamic three-phase electrical and mechanical power analysis and complete test coverage of the entire motor-drive system.
See the full story… |


 |

|

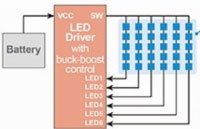
ROHM Semiconductor’s BD81A76EFV-M
LED driver IC. |
Backlight LED Driver Is Compatible With 3- To 12-in. Vehicle LCD Panels
 Diagram: The LED driver incorporates proprietary buck-boost control to provide greater application flexibility in LCD applications. While conventional LED drivers are only capable of driving 36 to 60 LEDs (6 to 10 LEDs/channel), the BD81A76EFV-M driver IC expands the range, driving from 6 to 60 LEDs (1 to 10 LEDs/channel). This ensures the support of not only larger displays but also small- and medium-size panels as well, using a single driver. Diagram: The LED driver incorporates proprietary buck-boost control to provide greater application flexibility in LCD applications. While conventional LED drivers are only capable of driving 36 to 60 LEDs (6 to 10 LEDs/channel), the BD81A76EFV-M driver IC expands the range, driving from 6 to 60 LEDs (1 to 10 LEDs/channel). This ensures the support of not only larger displays but also small- and medium-size panels as well, using a single driver.
See the full story…
|
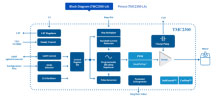
TRINAMIC’s TMC2300 motor driver IC.
|
Silent Motor Controller Enables Battery-Powered Stepper Motors To Run in Stealth Mode
 Photo: The stepper motor driver addresses key mobile design requirements and is said to offer a superior end-user experience by enabling virtually silent and vibration free operation. Applications range from IoT-connected devices and portable printers to wearable medical devices. Photo: The stepper motor driver addresses key mobile design requirements and is said to offer a superior end-user experience by enabling virtually silent and vibration free operation. Applications range from IoT-connected devices and portable printers to wearable medical devices.
 Diagram: In addition to silent stepper operation in motion and in standstill, the TMC-2300 offers benefits such as low-voltage operation from one or two Li-Ion cells or two double AA batteries; sensorless motor load measurement, eliminating the need for end-stop switches, performing sensorless homing and detecting mechanical obstacles; and high energy efficiency. Diagram: In addition to silent stepper operation in motion and in standstill, the TMC-2300 offers benefits such as low-voltage operation from one or two Li-Ion cells or two double AA batteries; sensorless motor load measurement, eliminating the need for end-stop switches, performing sensorless homing and detecting mechanical obstacles; and high energy efficiency.
See the full story…
|

ABSOPULSE Electronics’ HVI
2K-F6W series dc-dc converters.
|
800-V Input DC-DC Converters Deliver 2000 W
 Photo: Operating over a 700-V to 900-V input range, the dc-dc converters generate up to 2000 W of output power at 24 V, 28 V, 36 V, 48 V, 110 V or a custom value. Especially suitable for space- and weight-constrained applications, the converters measure 254 x 65 x 349 mm and weigh approx. 3.4 kg (7.5 lbs). Photo: Operating over a 700-V to 900-V input range, the dc-dc converters generate up to 2000 W of output power at 24 V, 28 V, 36 V, 48 V, 110 V or a custom value. Especially suitable for space- and weight-constrained applications, the converters measure 254 x 65 x 349 mm and weigh approx. 3.4 kg (7.5 lbs).
See the full story…
|

|







|
INDUSTRY EVENTS  |
|
Another Successful ECCE
The recently concluded IEEE Energy Conversion Congress & Expo (ECCE 2019), drew 1829 registered attendees to the Baltimore Convention Center, September 29-October 3. Participants from academia, industry and research institutions enjoyed an extensive program consisting of 18 tutorials, 18 special sessions and 1069 technical papers spread across 153 oral sessions and 20 poster sessions plus five plenary session talks. Attendees also toured a busy exhibition with the latest design tools, instruments and other products for power electronics and machine design, and viewed demos from top universities in these fields. Stay tuned for more post conference news. Next year’s ECCE will be held in Detroit, Michigan—the epicenter of the U.S. automotive industry. For those interested in presenting, ECCE 2020 has issued its Call for Papers, Call for Special Sessions and Call for Tutorials.
|

|

OTHER TOP POWER NEWS
|
|
 Teledyne LeCroy will present a two-part webinar on “Probing in Power Electronics: What to Use and Why”. Part 1 will be presented on October 23, 2019 to be followed by part 2 on October 30. Teledyne LeCroy will present a two-part webinar on “Probing in Power Electronics: What to Use and Why”. Part 1 will be presented on October 23, 2019 to be followed by part 2 on October 30.
 Power Integrations has announced the delivery of its one-millionth InnoSwitch3 switcher IC featuring the company’s PowiGaN gallium-nitride technology to Shenzhen-based Anker Innovations. Power Integrations has announced the delivery of its one-millionth InnoSwitch3 switcher IC featuring the company’s PowiGaN gallium-nitride technology to Shenzhen-based Anker Innovations.


 Cree has announced plans to establish a silicon carbide corridor on the east coast of the U.S. with the creation of the world’s largest SiC fabrication facility in upstate New York. Cree has announced plans to establish a silicon carbide corridor on the east coast of the U.S. with the creation of the world’s largest SiC fabrication facility in upstate New York.
 The Center of High Performance Power Electronics (CHPPE) at The Ohio State University (OSU) will hold its annual review event on November 17 to 19, 2019. The Center of High Performance Power Electronics (CHPPE) at The Ohio State University (OSU) will hold its annual review event on November 17 to 19, 2019.
 The IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo has issued a call for papers for next year’s conference (ITEC 2020), which will be held June 24-26, 2020 at the Navy Pier in Chicago. It has also issued a call for speakers for short course instructors, tutorial instructors and panel organizers & panelists. The IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference & Expo has issued a call for papers for next year’s conference (ITEC 2020), which will be held June 24-26, 2020 at the Navy Pier in Chicago. It has also issued a call for speakers for short course instructors, tutorial instructors and panel organizers & panelists.
 Advanced Energy Industries has completed its previously announced acquisition of Artesyn Embedded Technologies’ Embedded Power business. Advanced Energy Industries has completed its previously announced acquisition of Artesyn Embedded Technologies’ Embedded Power business.
|
ABOUT THIS NEWSLETTER: Thank you for reading HOW2POWER TODAY.
How2Power sends no more than one e-mail per month to registered users. Continuing your subscription ensures you'll receive future newsletters. Manage Your Subscription
©2019 All rights reserved. www.how2power.com
|
|